VSports最新版本 - Polymorphism of the PEMT gene and susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- PMID: 16051693
- PMCID: PMC1256033
- DOI: "V体育ios版" 10.1096/fj.04-3580com
VSports app下载 - Polymorphism of the PEMT gene and susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Abstract
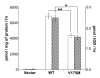
Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT) catalyzes phosphatidylcholine synthesis. PEMT knockout mice have fatty livers, and it is possible that, in humans, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) might be associated with PEMT gene polymorphisms. DNA samples from 59 humans without fatty liver and from 28 humans with NAFLD were genotyped for a single nucleotide polymorphism in exon 8 of PEMT, which leads to a V175M substitution. V175M is a loss of function mutation, as determined by transiently transfecting McArdle-RH7777 cells with constructs of wild-type PEMT open reading frame or the V175M mutant. Met/Met at residue 175 (loss of function SNP) occurred in 67. 9% of the NAFLD subjects and in only 40. 7% of control subjects (P<0. 03). For the first time we report that a polymorphism of the human PEMT gene (V175M) is associated with diminished activity and may confer susceptibility to NAFLD. VSports手机版.
Figures
Comment in
-
No association between polymorphism in PEMT (V175M) and hepatic triglyceride content in the Dallas Heart Study.FASEB J. 2006 Oct;20(12):2180; author reply 2181-2. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-1004ufm. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 17012264 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: definition and pathology. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Falck-Ytter Y, Younossi ZM, Marchesini G, McCullough AJ. Clinical features and natural history of nonalcoholic steatosis syndromes. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:17–26. - "V体育ios版" PubMed
-
- Zeisel SH, daCosta KA, Franklin PD, Alexander EA, Lamont JT, Sheard NF, Beiser A. Choline, an essential nutrient for humans. FASEB J. 1991;5:2093–2098. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Buchman A, Dubin M, Moukarzel A, Jenden D, Roch M, Rice K, Gornbein J, Ament M. Choline deficiency: a cause of hepatic steatosis during parenteral nutrition that can be reversed with intravenous choline supplementation. Hepatology. 1995;22:1399–1403. - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
Substances
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports" Actions
VSports - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports - Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

