Human peptidoglycan recognition protein S is an effector of neutrophil-mediated innate immunity
- PMID: 15956276
- PMCID: PMC1895263 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0530 (V体育安卓版)
"V体育2025版" Human peptidoglycan recognition protein S is an effector of neutrophil-mediated innate immunity
Abstract
Innate immune responses to bacteria require cooperative interactions between host recognition molecules and phagocytes. The peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs) are a large group of proteins found in insects and mammals that bind to bacterial peptidoglycan (PGN). PGRP-S is located with other antimicrobial proteins, such as lysozyme, in the granules of human neutrophils. Whereas both PGRP-S and lysozyme recognize PGN, the exact binding specificity of human PGRP-S, its functional activity, and its potential synergy with other neutrophil-derived bactericidal proteins such as lysozyme have not been determined. Here we show that human PGRP-S binds to and inhibits the growth of Staphylococcus aureus (containing lysine-type PGN) and Escherichia coli (containing mesodiaminopimelic acid-type PGN). The binding affinity and thus antimicrobial activity of PGRP-S is determined by the third amino acid in the PGN stem peptide. Furthermore, the antimicrobial effect of PGRP-S against E coli is synergistic with lysozyme, and lysozyme and PGRP-S colocalize in neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), suggesting that these granule-derived proteins act together to kill bacteria trapped in the NETs VSports手机版. Taken together, these results indicate that human PGRP-S plays a role in innate immunity in the context of neutrophils by contributing to the killing of intracellular and extracellular bacteria. .
Figures
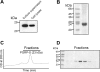


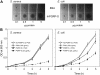
 ) or no additives (⋄). Tubes were shaken at 300 rpm for 5 hours, and bacterial density was monitored by measurement of optic density (OD) at 600 nm at 1-hour intervals. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments.
) or no additives (⋄). Tubes were shaken at 300 rpm for 5 hours, and bacterial density was monitored by measurement of optic density (OD) at 600 nm at 1-hour intervals. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments.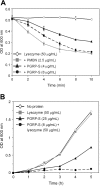
 ]), and the change in OD at 600 nm was monitored for 10 minutes. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. (B) Growth inhibition of E coli cells. E coli cells were incubated in 1 × TSB (3% wt/vol) with 50 μg/mL lysozyme (
]), and the change in OD at 600 nm was monitored for 10 minutes. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. (B) Growth inhibition of E coli cells. E coli cells were incubated in 1 × TSB (3% wt/vol) with 50 μg/mL lysozyme ( ), 25 μg/mL rhPGRP-S (▴), 8 μg/mL rhPGRP-S and 50 μg/mL of lysozyme (•), or no protein (⋄). Tubes were shaken at 300 rpm for 5 hours, and bacterial density was monitored by measurement of optic density (OD) at 600 nm at 1-hour intervals. Data represent the mean of duplicate samples from 1 of 2 similar experiments.
), 25 μg/mL rhPGRP-S (▴), 8 μg/mL rhPGRP-S and 50 μg/mL of lysozyme (•), or no protein (⋄). Tubes were shaken at 300 rpm for 5 hours, and bacterial density was monitored by measurement of optic density (OD) at 600 nm at 1-hour intervals. Data represent the mean of duplicate samples from 1 of 2 similar experiments.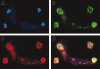
References
-
- Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway CA, Ezekowitz RAB. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science. 1999;284: 1313-1318. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20: 197-216. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann JA. The immune response of Drosophila. Nature. 2003;426: 33-38. - PubMed (V体育ios版)
-
- Yoshida H, Kinoshita K, Ashida M. Purification of a peptidoglycan recognition protein from hemolymph of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem. 1996;271: 13854-13860. - PubMed
-
- Ochiai M, Ashida M. A pattern recognition protein for peptidoglycan: cloning the cDNA and the gene of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem. 1999;274: 11854-11858. - VSports在线直播 - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports app下载)
MeSH terms (V体育官网)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Substances (VSports手机版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

