Identification and functional characterization of chicken toll-like receptor 5 reveals a fundamental role in the biology of infection with Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
- PMID: 15784580
- PMCID: PMC1087448
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.2344-2350.2005
Identification and functional characterization of chicken toll-like receptor 5 reveals a fundamental role in the biology of infection with Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium (V体育ios版)
Abstract
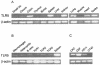
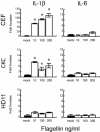
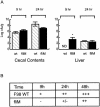
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a major component of the pattern recognition receptor repertoire that detect invading microorganisms and direct the vertebrate immune system to eliminate infection. In chickens, the differential biology of Salmonella serovars (systemic versus gut-restricted localization) correlates with the presence or absence of flagella, a known TLR5 agonist. Chicken TLR5 (chTLR5) exhibits conserved sequence and structural similarity with mammalian TLR5 and is expressed in tissues and cell populations of immunological and stromal origin. Exposure of chTLR5+ cells to flagellin induced elevated levels of chicken interleukin-1beta (chIL-1beta) but little upregulation of chIL-6 mRNA. Consistent with the flagellin-TLR5 hypothesis, an aflagellar Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium fliM mutant exhibited an enhanced ability to establish systemic infection. During the early stages of infection, the fliM mutant induced less IL-1beta mRNA and polymorphonuclear cell infiltration of the gut. Collectively, the data represent the identification and functional characterization of a nonmammalian TLR5 and indicate a role in restricting the entry of flagellated Salmonella into systemic sites of the chicken VSports手机版. .
Figures


References
-
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2:675-680. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Allen-Vercoe, E., and M. J. Woodward. 1999. Colonisation of the chicken caecum by afimbriate and aflagellate derivatives of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis. Vet. Microbiol. 69:265-275. - VSports - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Barrow, P. A., M. B. Huggins, M. A. Lovell, and J. M. Simpson. 1987. Observations on the pathogenesis of experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection in chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 42:194-199. - PubMed
-
- Barrow, P. A., M. A. Lovell, and B. A. D. Stocker. 2000. Protection against experimental fowl typhoid by parenteral administration of live SL5928, an aroA-serC (aromatic dependent) mutant of a wild-type Salmonella Gallinarum strain made lysogenic for P22e sie. Avian Pathol. 29:423-431. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

