VSports手机版 - Microsatellite instability regulates transcription factor binding and gene expression
- PMID: 15728391
- PMCID: "VSports手机版" PMC553301
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0406805102
Microsatellite instability regulates transcription factor binding and gene expression (VSports最新版本)
Abstract
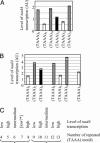
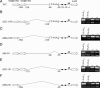
Microsatellites are tandemly repeated simple sequence DNA motifs widely prevalent in eukaryotic and prokaryotic genomes. In pathogenic bacteria, instability of these hypermutable loci through slipped-strand mispairing mediates the high-frequency reversible switching of phenotype expression, i. e VSports手机版. , phase variation. Phase-variable expression of NadA, an outer membrane protein and adhesin of the pathogen Neisseria meningitidis, is mediated by changes in the number of TAAA repeats located upstream of the core promoter of nadA. Here we report that loss or gain of TAAA repeats affects the binding of the transcriptional regulatory protein IHF to the nadA promoter. Thus, phase-variable transcription of nadA potentially incorporates interplay between stochastic (mutational) and prescriptive (classical) mechanisms of gene regulation. .
Figures

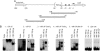

References (VSports在线直播)
-
- Johnson, C. R., Newcombe, J., Thorne, S., Borde, H. A., Eales-Reynolds, L. J., Gorringe, A. R., Funnell, S. G. & McFadden, J. J. (2001) Mol. Microbiol. 39, 1345-1355. - PubMed
-
- Deghmane, A. E., Giorgini, D., Larribe, M., Alonso, J. M. & Taha, M. K. (2002) Mol. Microbiol. 43, 1555-1564. - V体育官网 - PubMed
-
- Moxon, E. R., Rainey, P. B., Nowak, M. A. & Lenski, R. E. (1994) Curr. Biol. 4, 24-33. - PubMed (VSports手机版)
Publication types
- V体育官网 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances
- Actions (VSports)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

