Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities
- PMID: 15466561
- PMCID: "VSports app下载" PMC522057
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.10.6147-6156.2004
Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities
Abstract
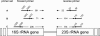
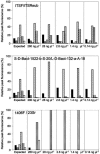
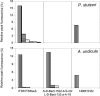
ITSF and ITSReub, constituting a new primer set designed for the amplification of the 16S-23S rRNA intergenic transcribed spacers, have been compared with primer sets consisting of 1406F and 23Sr (M. M. Fisher and E. W. Triplett, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65:4630-4636, 1999) and S-D-Bact-1522-b-S-20 and L-D-Bact-132-a-A-18 (L. Ranjard et al. , Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:4479-4487, 2001), previously proposed for automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis (ARISA) of complex bacterial communities. An agricultural soil and a polluted soil, maize silage, goat milk, a small marble sample from the facade of the Certosa of Pavia (Pavia, Italy), and brine from a deep hypersaline anoxic basin in the Mediterranean Sea were analyzed with the three primer sets. The number of peaks in the ARISA profiles, the range of peak size (width of the profile), and the reproducibility of results were used as indices to evaluate the efficiency of the three primer sets. The overall data showed that ITSF and ITSReub generated the most informative (in term of peak number) and reproducible profiles and yielded a wider range of spacer sizes (134 to 1,387) than the other primer sets, which were limited in detecting long fragments. The minimum amount of DNA template and sensitivity in detection of minor DNA populations were evaluated with artificial mixtures of defined bacterial species. ITSF and ITSReub amplified all the bacteria at DNA template concentrations from 280 to 0. 14 ng microl(-1), while the other primer sets failed to detect the spacers of one or more bacterial strains. Although the primer set consisting of ITSF and ITSReub and that of S-D-Bact-1522-b-S-20 and L-D-Bact-132-a-A-18 showed similar sensitivities for the DNA of Allorhizobium undicula mixed with the DNA of other species, the S-D-Bact-1522-b-S-20 and L-D-Bact-132-a-A-18 primer set failed to detect the DNA of Pseudomonas stutzeri. VSports手机版.
VSports - Figures
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1994. Current protocols of molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms (V体育官网)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports最新版本" Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

