Rapamycin inhibits GM-CSF-induced neutrophil migration (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 12935893
- PMCID: PMC3074563
- DOI: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00828-7
"VSports" Rapamycin inhibits GM-CSF-induced neutrophil migration
"V体育平台登录" Abstract
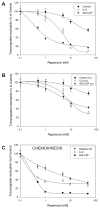
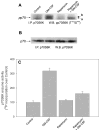
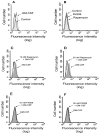
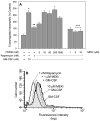
The molecular mechanisms that govern cell movement are the subject of intense study, as they impact biologically and medically important processes such as leukocyte chemotaxis and angiogenesis, among others. We demonstrate that leukocyte chemotaxis is prevented by the macrolide immunosuppressant rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/ribosomal p70-S6 kinase (p70S6K) pathway. Both neutrophil chemotaxis and chemokinesis elicited by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) were strongly inhibited by rapamycin with an IC(50) of 0. 3 nM. Inhibition, although at a higher dose, was also observed when the chemoattractant was interleukin-8. As for the mechanism, rapamycin targeted the increase of phosphorylation of p70S6K due to GM-CSF treatment, as demonstrated with specific anti-p70S6K immunoprecipitation and subsequent immunoblotting with anti-T(421)/S(424) antibodies. Rapamycin also inhibited GM-CSF-induced actin polymerization, a hallmark of leukocyte migration. The specificity of the effect of rapamycin was confirmed by the use of the structural analog FK506, which did not have a significant effect on chemotaxis but effectively rescued rapamycin-induced p70S6K inhibition VSports手机版. This was expected from a competitive effect of both molecules on FK506-binding proteins (FKBP). Additionally, GM-CSF-induced chemotaxis was completely (>90%) blocked by a combination of rapamycin and the MAPK kinase (MEK) inhibitor PD-98059. In summary, the results presented here indicate for the first time that rapamycin, at sub-nanomolar concentrations, inhibits GM-CSF-induced chemotaxis and chemokinesis. This serves to underscore the relevance of the mTOR/S6K pathway in neutrophil migration. .
Figures (VSports app下载)
References
-
- Sasaki T, Irie-Sasaki J, Jones RG, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Stanford WL, Bolon B, Wakeham A, Itie A, Bouchard D, Kozieradzki I, Joza N, Mak TW, Ohashi PS, Suzuki A, Penninger JM. Science. 2000;287:1040–1046. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Li Z, Jiang H, Xie W, Zhang Z, Smrcka AV, Wu D. Science. 2000;287:1046–1049. - VSports app下载 - PubMed
-
- Nijhuis E, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ. J Leukocyte Biol. 2002;71:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Crouch MF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;233:193–199. - PubMed
Publication types (VSports)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
V体育2025版 - MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
"VSports最新版本" Substances
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Grants and funding (V体育2025版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (VSports在线直播)
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (V体育2025版)

