"V体育官网" A human minor histocompatibility antigen resulting from differential expression due to a gene deletion
- PMID: 12743171
- PMCID: PMC2193779
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030044
A human minor histocompatibility antigen resulting from differential expression due to a gene deletion
Abstract
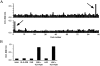
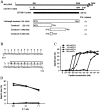
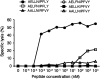
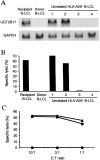
Minor histocompatibility antigens (minor H antigens) are targets of graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia responses after allogeneic human leukocyte antigen identical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Only a few human minor H antigens have been molecularly characterized and in all cases, amino acid differences between homologous donor and recipient proteins due to nucleotide polymorphisms in the respective genes were responsible for immunogenicity. Here, we have used cDNA expression cloning to identify a novel human minor H antigen encoded by UGT2B17, an autosomal gene in the multigene UDP-glycosyltransferase 2 family that is selectively expressed in liver, intestine, and antigen-presenting cells. In contrast to previously defined human minor H antigens, UGT2B17 is immunogenic because of differential expression of the protein in donor and recipient cells as a consequence of a homozygous gene deletion in the donor. Deletion of individual members of large gene families is a common form of genetic variation in the population and our results provide the first evidence that differential protein expression as a consequence of gene deletion is a mechanism for generating minor H antigens in humans VSports手机版. .
Figures

References
-
- Storb, R., H.J. Deeg, J. Whitehead, F. Appelbaum, P. Beatty, W. Bensinger, C.D. Buckner, R. Clift, K. Doney, V. Farewell, et al. 1986. Methotrexate and cyclosporine compared with cyclosporine alone for prophylaxis of acute graft versus host disease after marrow transplantation for leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 314:729–735. - PubMed
-
- Goulmy, E. 1997. Human minor histocompatibility antigens: new concepts for marrow transplantation and adoptive immunotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 157:125–140. - PubMed
-
- Warren, E.H., M. Gavin, P.D. Greenberg, and S.R. Riddell. 1998. Minor histocompatibility antigens as targets for T-cell therapy after bone marrow transplantation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 5:429–433. - PubMed
-
- Malarkannan, S., T. Horng, P. Eden, F. Gonzalez, P. Shih, N. Brouwenstijn, H. Klinge, G. Christianson, D. Roopenian, and N. Shastri. 2000. Differences that matter: major cytotoxic T cell-stimulating minor histocompatibility antigens. Immunity. 13:333–344. - PubMed
-
- Wang, W., L.R. Meadows, J.M. den Haan, N.E. Sherman, Y. Chen, E. Blokland, J. Shabanowitz, A.I. Agulnik, R.C. Hendrickson, C.E. Bishop, et al. 1995. Human H-Y: a male-specific histocompatibility antigen derived from the SMCY protein. Science. 269:1588–1590. - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
VSports - Publication types
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
"V体育官网" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports手机版" Other Literature Sources

