Mutations in COX15 produce a defect in the mitochondrial heme biosynthetic pathway, causing early-onset fatal hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 12474143
- PMCID: PMC378614 (VSports)
- DOI: 10.1086/345489
Mutations in COX15 produce a defect in the mitochondrial heme biosynthetic pathway, causing early-onset fatal hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
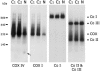
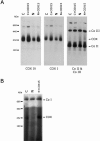
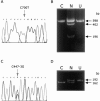
Deficiencies in the activity of cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal enzyme in the respiratory chain, are a frequent cause of autosomal recessive mitochondrial disease in infants. These patients are clinically and genetically heterogeneous, and all defects so far identified in this group have been found in genes coding for accessory proteins that play important roles in the assembly of the COX holoenzyme complex. Many patients, however, remain without a molecular diagnosis. We have used a panel of retroviral vectors expressing human COX assembly factors in these patients to identify the molecular basis for the COX deficiency by functional complementation. Here we show that overexpression of COX15, a protein involved in the synthesis of heme A, the heme prosthetic group for COX, can functionally complement the isolated COX deficiency in fibroblasts from a patient with fatal, infantile hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Mutation analysis of COX15 in the patient identified a missense mutation (C700T) on one allele, changing a conserved arginine to tryptophan (R217W), and a splice-site mutation in intron 3 on the other allele (C447-3G), resulting in a deletion of exon 4. This splicing error introduces a frameshift and a premature stop codon, resulting in an unstable mRNA and, likely, a null allele. Mitochondrial heme A content was reduced in the patient's heart and fibroblast mitochondria, and levels of heme O were increased in the patient's heart. COX activity and the total amount of fully assembled enzyme were reduced by 50%-70% in patient fibroblasts. Expression of COX15 increased heme A content and rescued COX activity VSports手机版. These results suggest that reduced availability of heme A stalls the assembly of COX. This study establishes COX15 as an additional cause, along with SCO2, of fatal infantile, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated with isolated COX deficiency. .
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- dbSNP, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=SNP (for the T1171C polymorphism [rs2231687])
-
- GenBank, V体育平台登录 - http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for the COX15.1 variant mRNA sequence [NM_078470] and COX15.2 variant mRNA sequence [NM_004376])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for cytochrome c oxidase deficiency [MIM 220110], SCO2 mutations [MIM 602472 and MIM 604377], and COX15 [MIM 603646])
References
-
- Barrientos A, Barros MH, Valnot I, Rotig A, Rustin P, Tzagoloff A (2002) Cytochrome oxidase in health and disease. Gene 286:53–63 - PubMed
-
- Barros MH, Carlson CG, Glerum DM, Tzagoloff A (2001) Involvement of mitochondrial ferredoxin and Cox15p in hydroxylation of heme O. FEBS Lett 492:133–138 - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Barros MH, Nobrega FG, Tzagoloff A (2002) Mitochondrial ferredoxin is required for heme A synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 277:9997–10002 - PubMed
-
- Barros MH, Tzagoloff A (2002) Regulation of the heme A biosynthetic pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 516:119–123 - PubMed (VSports app下载)
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254 - PubMed (VSports app下载)
Publication types
- Actions (VSports)
"V体育官网入口" MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Associated data
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources (VSports在线直播)
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

