Biodiversity of the bacterial flora on the surface of a smear cheese
- PMID: 11823224
- PMCID: PMC126715
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.2.820-830.2002
V体育安卓版 - Biodiversity of the bacterial flora on the surface of a smear cheese
"VSports最新版本" Abstract
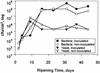
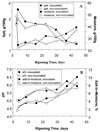
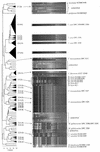
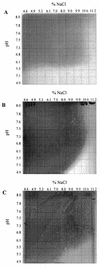
The bacteria on the surface of a farmhouse smear-ripened cheese at four stages of ripening (4, 16, 23, and 37 days) from inoculated (i. e. , deliberately inoculated with Brevibacterium linens BL2) and noninoculated (not deliberately inoculated with B. linens BL2) cheese were investigated. The results show that, contrary to accepted belief, B. linens is not a significant member of the surface flora of smear cheese and no microbial succession of species occurred during the ripening of the cheeses. Of 400 isolates made, 390 were lactate-utilizing coryneforms and 10 were coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. A detailed analysis of the coryneforms was undertaken using phenotypic analysis, molecular fingerprinting, chemotaxonomic techniques, and 16S rRNA gene sequencing. DNA banding profiles (ramdom amplified polymorphic DNA [RAPD]-PCR) of all the coryneform isolates showed large numbers of clusters. However, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) of the isolates from the cheeses showed that all isolates within a cluster and in many contiguous clusters were the same. The inoculated and noninoculated cheeses were dominated by single clones of novel species of Corynebacterium casei (50. 2% of isolates), Corynebacterium mooreparkense (26% of isolates), and Microbacterium gubbeenense (12. 8% of isolates). In addition, five of the isolates from the inoculated cheese were Corynebacterium flavescens. Thirty-seven strains were not identified but many had similar PFGE patterns, indicating that they were the same species. C VSports手机版. mooreparkense and C. casei grew at pH values below 4. 9 in the presence of 8% NaCl, while M. gubbeenense did not grow below pH 5. 8 in the presence of 5 to 10% NaCl. B. linens BL2 was not recovered from the inoculated cheese because it was inhibited by all the Staphylococcus isolates and many of the coryneforms. It was concluded that within a particular batch of cheese there was significant bacterial diversity in the microflora on the surface. .
Figures


"V体育2025版" References
-
- Brennan, N. M., R. Brown, M. Goodfellow, A. C. Ward, T. P. Beresford, P. J. Simpson, P. F. Fox, and T. M. Cogan. 2001. Corynebacterium mooreparkense sp. nov., and Corynebacterium casei sp. nov. isolated from the surface of a smear-ripened cheese. Int. J. Syst. E vol. Microbiol. 51:843-852. - PubMed
-
- Brennan, N. M., R. Brown, M. Goodfellow, A. C. Ward, T. P. Beresford, M. Vancanneyt, T. M. Cogan, and P. F. Fox. 2001. Microbacterium gubbeenense sp. nov., isolated from the surface of a smear-ripened cheese. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1969-1976. - PubMed
-
- Busse, M. 1989. Die Oberflachenflora von Geschmierten Käse. Milchwirt. Berichte. 99:137-141.
-
- Cure, G. L., and R. M. Keddie. 1973. Methods for the morphological examination of aerobic coryneform bacteria, p. 123-135. In R. G. Board and D. W. Lovelock (ed.), Sampling—microbiological monitoring of environments—1973. Academic Press, London, United Kingdom.
-
- El-Erian, A. F. M. 1969. Bacteriological studies on limburger cheese. Ph.D. thesis. Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

