Shiga toxins induce, superinduce, and stabilize a variety of C-X-C chemokine mRNAs in intestinal epithelial cells, resulting in increased chemokine expression
- PMID: 11553553
- PMCID: PMC98744
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6140-6147.2001
Shiga toxins induce, superinduce, and stabilize a variety of C-X-C chemokine mRNAs in intestinal epithelial cells, resulting in increased chemokine expression
Abstract
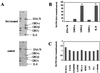
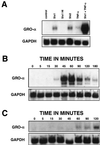
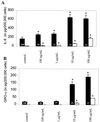
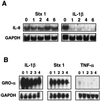
Exposure of humans to Shiga toxins (Stxs) is a risk factor for hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS). Because Stx-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) is a noninvasive enteric pathogen, the extent to which Stxs can cross the host intestinal epithelium may affect the risk of developing HUS. We have previously shown that Stxs can induce and superinduce IL-8 mRNA and protein in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) in vitro via a ribotoxic stress response. We used cytokine expression arrays to determine the effect of Stx1 on various C-X-C chemokine genes in IECs. We observed that Stx1 induces multiple C-X-C chemokines at the mRNA level, including interleukin-8 (IL-8), GRO-alpha, GRO-beta, GRO-gamma, and ENA-78. Like that of IL-8, GRO-alpha and ENA-78 mRNAs are both induced and superinduced by Stx1. Furthermore, Stx1 induces both IL-8 and GRO-alpha protein in a dose-response fashion, despite an overall inhibition in host cell protein synthesis. Stx1 treatment stabilizes both IL-8 and GRO-alpha mRNA. We conclude that Stxs are able to increase mRNA and protein levels of multiple C-X-C chemokines in IECs, with increased mRNA stability at least one mechanism involved. We hypothesize that ribotoxic stress is a pathway by which Stxs can alter host signal transduction in IECs, resulting in the production of multiple chemokine mRNAs, leading to increased expression of specific proteins VSports手机版. Taken together, these data suggest that exposing IECs to Stxs may stimulate a proinflammatory response, resulting in influx of acute inflammatory cells and thus contributing to the intestinal tissue damage seen in STEC infection. .
Figures

References
-
- Acheson D W K. Effect of Shiga toxins on cytokine production from intestinal epithelial cells. In: Keusch G T, Kawakami M, editors. Cytokines, cholera, and the gut. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: IOS Press; 1996. pp. 67–73.
-
- Blake D C I, Russell R G, Santini E, Bowen T, Boedeker E C. Pro-inflammatory mucosal cytokine responses to Shiga-like toxin-1 (SLT-1) In: Keusch G T, Kawakami M, editors. Cytokines, cholera, and the gut. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: IOS Press; 1996. pp. 75–82.
-
- Church G M, Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81:1991–1995. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Cochran B H, Refuel A C, Stiles C D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet derived growth factor. Cell. 1983;33:939–947. - PubMed
"V体育安卓版" Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
VSports app下载 - Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

