Salmonella-induced cell death is not required for enteritis in calves (V体育2025版)
- PMID: 11402005
- PMCID: PMC98538 (V体育2025版)
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4610-4617.2001
Salmonella-induced cell death is not required for enteritis in calves
Abstract (V体育2025版)
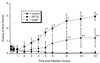
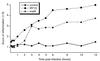
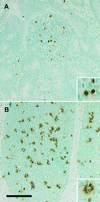
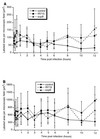
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium causes cell death in bovine monocyte-derived and murine macrophages in vitro by a sipB-dependent mechanism. During this process, SipB binds and activates caspase-1, which in turn activates the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1beta through cleavage. We used bovine ileal ligated loops to address the role of serovar Typhimurium-induced cell death in induction of fluid accumulation and inflammation in this diarrhea model. Twelve perinatal calves had 6- to 9-cm loops prepared in the terminal ileum. They were divided into three groups: one group received an intralumen injection of Luria-Bertani broth as a control in 12 loops. The other two groups (four calves each) were inoculated with 0. 75 x 10(9) CFU of either wild-type serovar Typhimurium (strain IR715) or a sopB mutant per loop in 12 loops VSports手机版. Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections were scored for inflammation, and terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells were detected in situ. Fluid accumulation began at 3 h postinfection (PI). Inflammation was detected in all infected loops at 1 h PI. The area of TUNEL-labeled cells in the wild-type infected loops was significantly higher than that of the controls at 12 h PI, when a severe inflammatory response and tissue damage had already developed. The sopB mutant induced the same amount of TUNEL-positive cells as the wild type, but it was attenuated for induction of fluid secretion and inflammation. Our results indicate that serovar Typhimurium-induced cell death is not required to trigger an early inflammatory response and fluid accumulation in the ileum. .
Figures


References
-
- Ahmer B M, van Reeuwijk J, Watson P R, Wallis T S, Heffron F. Salmonella SirA is a global regulator of genes mediating enteropathogenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1999;31:971–982. - PubMed
-
- Baran J, Guzik K, Hryniewicz W, Ernst M, Flad H D, Pryjma J. Apoptosis of monocytes and prolonged survival of granulocytes as a result of phagocytosis of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1996;64:4242–4248. - "V体育2025版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Brennan M A, Cookson B T. Salmonella induces macrophage death by caspase-1-dependent necrosis. Mol Microbiol. 2000;38:31–40. - PubMed (V体育2025版)
-
- Chen L M, Kaniga K, Galán J E. Salmonella spp. are cytotoxic for cultured macrophages. Mol Microbiol. 1996;21:1101–1115. - "V体育安卓版" PubMed
-
- Conover W J. Practical nonparametric statistics. New York, N.Y: Wiley; 1980.
Publication types
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
"VSports在线直播" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

