Murine gammaherpesvirus-68 infection causes multi-organ fibrosis and alters leukocyte trafficking in interferon-gamma receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 11395389
- PMCID: PMC1892003
- DOI: VSports最新版本 - 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64683-4
Murine gammaherpesvirus-68 infection causes multi-organ fibrosis and alters leukocyte trafficking in interferon-gamma receptor knockout mice (VSports最新版本)
VSports - Abstract
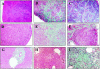
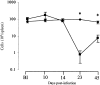
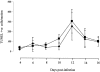
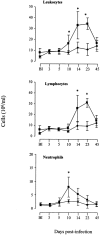
Murine gammaherpesvirus-68 (MHV-68) infection in interferon-gamma receptor knockout mice (IFN-gammaR(-)/(-)) results in splenic fibrosis and excessive loss of splenocytes. In our present study we found that MHV-68 infection in IFN-gammaR(-)/(-) mice also resulted in fibrosis and atrophy of the mediastinal lymph nodes, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and fibrotic changes in the liver. Atrophy and cellular depletion of the spleen in IFN-gammaR(-)/(-) was not the result of increased cell death. The loss of splenocytes in IFN-gammaR(-)/(-) mice, which was most evident on day 23 after infection, correlated with an increase in the number of leukocytes in peripheral blood. At the peak of leukocytosis, on day 23 after infection, peripheral blood cells from infected IFN-gammaR(-)/(-) mice were unable to traffic through the fibrosed spleens of IFN-gammaR(-)/(-) mice but were able to enter the spleens of wild-type mice. This indicates that leukocytosis was in part the result of emigration of cells from the spleen and their subsequent exclusion of re-entry at the height of fibrosis. Significant cytokine and chemokine changes were observed in spleens of IFN-gammaR(-)/(-) mice. IFN-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha ), TNF-beta, interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), lymphotactin, and MIP-1beta were elevated on day 14 after infection whereas chemokines IP-10 and MIG were significantly reduced VSports手机版. These changes suggest a role for dysregulated cytokines and chemokines in severe organ-specific fibrosis with implications for immune-mediated fibrotic disorders. .
Figures

References
-
- Speck SH, Virgin HW: Host and viral genetics of chronic infection: a mouse model of gamma-herpesvirus pathogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol 1999, 2:403-409 - PubMed
-
- Sunil-Chandra NP, Efstathiou S, Nash AA: Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 establishes a latent infection in mouse B lymphocytes in vivo. J Gen Virol 1992, 73:3275-3279 - VSports注册入口 - PubMed
-
- Sunil-Chandra NP, Efstathiou S, Arno J, Nash AA: Virological and pathological features of mice infected with murine gamma-herpesvirus 68. J Gen Virol 1992, 73:2347-2356 - PubMed
"VSports最新版本" Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
"V体育2025版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网)
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

