Functional genomic, biochemical, and genetic characterization of the Salmonella pduO gene, an ATP:cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase gene
- PMID: 11160088
- PMCID: PMC95042 (V体育官网入口)
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.5.1577-1584.2001
Functional genomic, biochemical, and genetic characterization of the Salmonella pduO gene, an ATP:cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase gene
Abstract
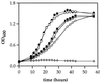
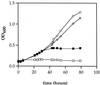
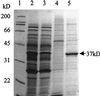
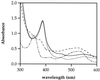
Salmonella enterica degrades 1,2-propanediol by a pathway dependent on coenzyme B12 (adenosylcobalamin [AdoCb1]) VSports手机版. Previous studies showed that 1,2-propanediol utilization (pdu) genes include those for the conversion of inactive cobalamins, such as vitamin B12, to AdoCbl. However, the specific genes involved were not identified. Here we show that the pduO gene encodes a protein with ATP:cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase activity. The main role of this protein is apparently the conversion of inactive cobalamins to AdoCbl for 1,2-propanediol degradation. Genetic tests showed that the function of the pduO gene was partially replaced by the cobA gene (a known ATP:corrinoid adenosyltransferase) but that optimal growth of S. enterica on 1,2-propanediol required a functional pduO gene. Growth studies showed that cobA pduO double mutants were unable to grow on 1,2-propanediol minimal medium supplemented with vitamin B(12) but were capable of growth on similar medium supplemented with AdoCbl. The pduO gene was cloned into a T7 expression vector. The PduO protein was overexpressed, partially purified, and, using an improved assay procedure, shown to have cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase activity. Analysis of the genomic context of genes encoding PduO and related proteins indicated that particular adenosyltransferases tend to be specialized for particular AdoCbl-dependent enzymes or for the de novo synthesis of AdoCbl. Such analyses also indicated that PduO is a bifunctional enzyme. The possibility that genes of unknown function proximal to adenosyltransferase homologues represent previously unidentified AdoCbl-dependent enzymes is discussed. .
Figures

References (VSports在线直播)
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Madden T L, Schäffer A A, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman D J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. - PMC (V体育安卓版) - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz D, Hushon J, Whitfield H, Jr, Roth J, Ames B. Procedure for identifying nonsense mutations. J Bacteriol. 1968;96:215–220. - PMC (VSports) - PubMed
-
- Bobik T A, Ailion M E, Roth J R. A single regulatory gene integrates control of vitamin B12 synthesis and propanediol degradation. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:2253–2266. - VSports在线直播 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Substances
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Associated data
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育官网" Molecular Biology Databases

