Mast cells control neutrophil recruitment during T cell-mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions through tumor necrosis factor and macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 11085746
- PMCID: VSports app下载 - PMC2193186
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.10.1441
"V体育官网" Mast cells control neutrophil recruitment during T cell-mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions through tumor necrosis factor and macrophage inflammatory protein 2
Abstract
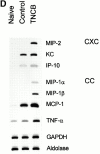
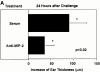
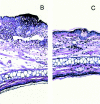
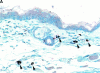
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) characterize the pathology of T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases and delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions (DTHRs) in the skin, joints, and gut, but are absent in T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases of the brain or pancreas. All of these reactions are mediated by interferon gamma-producing type 1 T cells and produce a similar pattern of cytokines. Thus, the cells and mediators responsible for the PMN recruitment into skin, joints, or gut during DTHRs remain unknown. Analyzing hapten-induced DTHRs of the skin, we found that mast cells determine the T cell-dependent PMN recruitment through two mediators, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and the CXC chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2), the functional analogue of human interleukin 8. Extractable MIP-2 protein was abundant during DTHRs in and around mast cells of wild-type (WT) mice but absent in mast cell-deficient WBB6F(1)-Kit(W)/Kit(W-)(v) (Kit(W)/Kit(W)(-v)) mice. T cell-dependent PMN recruitment was reduced >60% by anti-MIP-2 antibodies and >80% in mast cell-deficient Kit(W)/Kit(W)(-v) mice. Mast cells from WT mice efficiently restored DTHRs and MIP-2-dependent PMN recruitment in Kit(W)/Kit(W)-(v) mice, whereas mast cells from TNF(-/)- mice did not VSports手机版. Thus, mast cell-derived TNF and MIP-2 ultimately determine the pattern of infiltrating cells during T cell-mediated DTHRs. .
VSports最新版本 - Figures










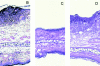


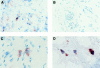
References
-
- Burmester G.R., Daser A., Kamradt T., Krause A., Mitchison N.A., Sieper J., Wolf N. Immunology of reactive arthritides. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1995;13:229–250. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M., Brennan F.M., Maini R.N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
-
- Edwards S.W., Hallett M.B. Seeing the wood for the treesthe forgotten role of neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Today. 1997;18:320–324. - PubMed
-
- Strober W., Ehrhardt R.O. Chronic intestinal inflammationan unexpected outcome in cytokine or T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1993;75:203–205. - PubMed
-
- Romagnani S. Th1/Th2 cells. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 1999;5:285–294. - V体育ios版 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育官网 - Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
V体育平台登录 - Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育ios版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

