Passive or active immunization with myelin basic protein promotes recovery from spinal cord contusion (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 10964948
- PMCID: PMC6772980 (V体育安卓版)
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-17-06421.2000 (VSports)
Passive or active immunization with myelin basic protein promotes recovery from spinal cord contusion
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2016 Feb 10;36(6):2075
Abstract
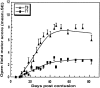
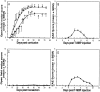
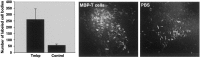
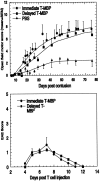
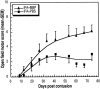
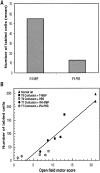
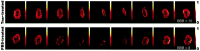
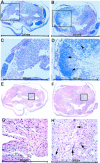
Partial injury to the spinal cord can propagate itself, sometimes leading to paralysis attributable to degeneration of initially undamaged neurons. We demonstrated recently that autoimmune T cells directed against the CNS antigen myelin basic protein (MBP) reduce degeneration after optic nerve crush injury in rats. Here we show that not only transfer of T cells but also active immunization with MBP promotes recovery from spinal cord injury. Anesthetized adult Lewis rats subjected to spinal cord contusion at T7 or T9, using the New York University impactor, were injected systemically with anti-MBP T cells at the time of contusion or 1 week later. Another group of rats was immunized, 1 week before contusion, with MBP emulsified in incomplete Freund's adjuvant (IFA). Functional recovery was assessed in a randomized, double-blinded manner, using the open-field behavioral test of Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan. The functional outcome of contusion at T7 differed from that at T9 (2. 9+/-0. 4, n = 25, compared with 8. 3+/-0. 4, n = 12; p<0. 003). In both cases, a single T cell treatment resulted in significantly better recovery than that observed in control rats treated with T cells directed against the nonself antigen ovalbumin. Delayed treatment with T cells (1 week after contusion) resulted in significantly better recovery (7. 0+/-1; n = 6) than that observed in control rats treated with PBS (2. 0+/-0. 8; n = 6; p<0. 01; nonparametric ANOVA). Rats immunized with MBP obtained a recovery score of 6. 1+/-0. 8 (n = 6) compared with a score of 3. 0+/-0. 8 (n = 5; p<0. 05) in control rats injected with PBS in IFA. Morphometric analysis, immunohistochemical staining, and diffusion anisotropy magnetic resonance imaging showed that the behavioral outcome was correlated with tissue preservation. The results suggest that T cell-mediated immune activity, achieved by either adoptive transfer or active immunization, enhances recovery from spinal cord injury by conferring effective neuroprotection VSports手机版. The autoimmune T cells, once reactivated at the lesion site through recognition of their specific antigen, are a potential source of various protective factors whose production is locally regulated. .
"VSports最新版本" Figures


"VSports" References
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. Graded histological and locomotor outcomes after spinal cord contusion using the NYU weight-drop device versus transection. Exp Neurol. 1996;139:244–256. - "V体育官网入口" PubMed
-
- Bavetta S, Hamlyn PJ, Burnstock G, Lieberman AR, Anderson PN. The effects of FK506 on dorsal column axons following spinal cord injury in adult rats: neuroprotection and local regeneration. Exp Neurol. 1999;158:382–393. - PubMed
-
- Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC, Komon J, Tovar CA, Van Meter M, Anderson DK, Faden AI, Hsu CY, Noble LJ, Salzman S, Young W. Endogenous repair after spinal cord contusion injuries in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1997;148:453–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
VSports注册入口 - Substances
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育平台登录)
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
