The c-Myc transactivation domain is a direct modulator of apoptotic versus proliferative signals
- PMID: 10825194
- PMCID: PMC85798
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.12.4309-4319.2000
The c-Myc transactivation domain is a direct modulator of apoptotic versus proliferative signals
Abstract
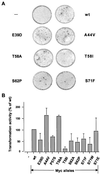
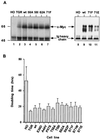
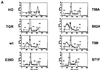
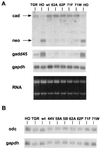
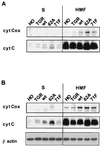
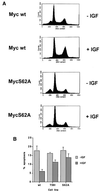
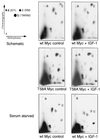
We have assayed the oncogenic, proliferative, and apoptotic activities of the frequent mutations that occur in the c-myc gene in Burkitt's lymphomas. Some alleles have a modest (50 to 60%) increase in transforming activity; however, the most frequent Burkitt's lymphoma allele (T58I) had an unexpected substantial decrease in transforming activity (85%). All alleles restored the proliferation function of c-Myc in cells that grow slowly due to a c-myc knockout. There was discordance for some alleles between apoptotic and oncogenic activities, but only the T58A allele had elevated transforming activity with a concomitant reduced apoptotic potential. We discovered a novel missense mutation, MycS71F, that had a very low apoptotic activity compared to wild-type Myc, yet this mutation has never been found in lymphomas, suggesting that there is no strong selection for antiapoptotic c-Myc alleles. MycS71F also induced very low levels of cytochrome c release from mitochondria, suggesting a mechanism of action for this mutation. Phosphopeptide mapping provided a biochemical basis for the dramatically different biological activities of the transformation-defective T58I and transformation-enhanced T58A c-Myc alleles. Furthermore, the antiapoptotic survival factor insulin-like growth factor 1 was found to suppress phosphorylation of T58, suggesting that the c-Myc transactivation domain is a direct target of survival signals. VSports手机版.
"V体育ios版" Figures


References
-
- Albert T, Urlbauer B, Kohlhuber F, Hammersen B, Eick D. Ongoing mutations in the N-terminal domain of c-Myc affect transactivation in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1994;9:759–763. - PubMed
-
- Alverez E, Northwood I, Gonzalez F, Latour D, Seth A, Abate C, Curran T, Davis R. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:15277–15285. - PubMed
-
- Askew D S, Ashmun R A, Simmons B C, Cleveland J L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991;6:1915–1922. - PubMed
-
- Beijersbergen R L, Hijmans E M, Zhu L, Bernards R. Interaction of c-Myc with the pRb-related protein p107 results in inhibition of c-Myc-mediated transactivation. EMBO J. 1994;13:4080–4086. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatia K, Huppi K, Spangler G, Siwarski D, Iyer R, Magrath I. Point mutations in the c-Myc transactivation domain are common in Burkitt's lymphoma and mouse plasmacytomas. Nat Genet. 1993;5:56–61. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (VSports)
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
