IL-11 separates graft-versus-leukemia effects from graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation
- PMID: 10430613
- PMCID: PMC408425
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI7111
"VSports最新版本" IL-11 separates graft-versus-leukemia effects from graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation
Abstract
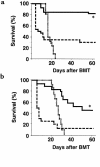
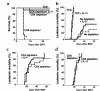
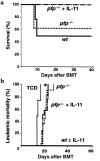
We recently showed that IL-11 prevents lethal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in a murine bone marrow transplantation (BMT) model of GVHD directed against MHC and minor antigens. In this study, we have investigated whether IL-11 can maintain a graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect. Lethally irradiated B6D2F1 mice were transplanted with either T cell-depleted (TCD) bone marrow (BM) alone or with BM and splenic T cells from allogeneic B6 donors. Animals also received host-type P815 mastocytoma cells at the time of BMT. Recipients were injected subcutaneously with recombinant human IL-11 or control diluent twice daily, from 2 days before BMT to 7 days after BMT. TCD recipients all died from leukemia by day 23. All control- and IL-11-treated allogeneic animals effectively rejected their leukemia, but IL-11 also reduced GVHD-related mortality. Examination of the cellular mechanisms of GVL and GVHD in this system showed that IL-11 selectively inhibited CD4-mediated GVHD, while retaining both CD4- and CD8-mediated GVL. In addition, IL-11 treatment did not affect cytolytic effector functions of T cells after BMT either in vivo or in vitro VSports手机版. Studies with perforin-deficient donor T cells demonstrated that the GVL effect was perforin dependent. These data demonstrated that IL-11 can significantly reduce CD4-dependent GVHD without impairing cytolytic function or subsequent GVL activity of CD8(+) T cells. Brief treatment with IL-11 shortly after BMT may therefore represent a novel strategy for separating GVHD and GVL. .
Figures
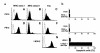
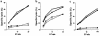
References
-
- Bortin M, Rimm A, Saltzstein E. Graft-versus-leukemia: Quantification of adoptive immunotherapy in murine leukemia. Science. 1973;173:811–813. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Truitt RJ, Johnson BD. Principles of graft versus leukemia reactivity. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;1:61–68. - PubMed
-
- Barrett AJ. Mechanisms of the graft-versus-leukemia reaction. Stem Cells. 1997;15:248–258. - PubMed
-
- Barnes D, Corp M, Loutit J, Neal F. Treatment of murine leukaemia with x-rays and homologous bone marrow: preliminary communication. Br Med J. 1956;2:626–630. - "V体育官网入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Horowitz MM, et al. Graft-verus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1990;75:555–562. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
V体育官网 - Research Materials

