Growth phase-regulated induction of Salmonella-induced macrophage apoptosis correlates with transient expression of SPI-1 genes
- PMID: 10348855
- PMCID: PMC93810 (V体育官网)
- DOI: V体育官网入口 - 10.1128/JB.181.11.3433-3437.1999
VSports - Growth phase-regulated induction of Salmonella-induced macrophage apoptosis correlates with transient expression of SPI-1 genes
Abstract
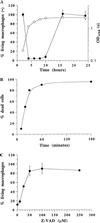
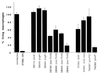
Invasive Salmonella has been reported to induce apoptosis in a fraction of infected macrophages within 2 to 14 h from the time of infection by a mechanism involving the type III secretion machinery encoded by the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1). Here, we show that bacteria in the transition from logarithmic to stationary phase cause 90% of the macrophages to undergo phagocytosis-independent, caspase-mediated apoptosis within 30 to 60 min of infection. The ability of Salmonella to induce this rapid apoptosis was growth phase regulated and cell type restricted, with epithelial cells being resistant. Apoptosis induction was also abrogated by disruption of the hilA gene (encoding a regulator of SPI-1 genes) and by the expression of a constitutively active PhoPQ. hilA itself and a subset of SPI-1 genes were transiently expressed during aerobic growth in liquid medium. Interestingly, however, hilA was found to be required only for the expression of the prgH gene, while sipB, invA, and invF were expressed in a hilA-independent manner. The expression of SPI-1 genes and the secretion of invasion-associated proteins correlated temporally with the induction of apoptosis and are likely to represent its molecular basis VSports手机版. Thus, growth phase transition regulates the expression and secretion of virulence determinants and represents the most efficient environmental cue for apoptosis induction reported to date. .
Figures (VSports)


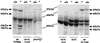
References
-
- Bajaj V, Lucas R L, Hwang C, Lee C A. Coordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:703–714. - VSports - PubMed
-
- Bajaj V, Hwang C, Lee C A. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:715–727. - V体育平台登录 - PubMed
-
- Boyd E F, Wang F-S, Whittam T S, Selander R K. Molecular genetic relationships of the salmonellae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:804–808. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen L M, Kaniga K, Galán J E. Salmonella spp. are cytotoxic for cultured macrophages. Mol Microbiol. 1996;21:1101–1115. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Smith M R, Thirumalai K, Zychlinsky A. A bacterial invasin induces macrophage apoptosis by binding directly to ICE. EMBO J. 1996;15:3853–3860. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
Substances (VSports在线直播)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

