GMAP-210, A cis-Golgi network-associated protein, is a minus end microtubule-binding protein (VSports最新版本)
- PMID: 10189370
- PMCID: PMC2148210
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.1.83
"V体育2025版" GMAP-210, A cis-Golgi network-associated protein, is a minus end microtubule-binding protein
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol 2002 Aug 5;158(3):593
Abstract
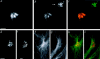
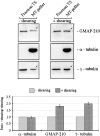
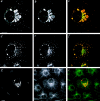
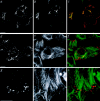
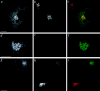
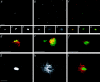
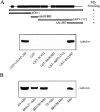
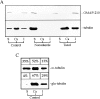
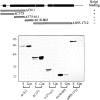
We report that a peripheral Golgi protein with a molecular mass of 210 kD localized at the cis-Golgi network (Rios, R. M VSports手机版. , A. M. Tassin, C. Celati, C. Antony, M. C. Boissier, J. C. Homberg, and M. Bornens. 1994. J. Cell Biol. 125:997-1013) is a microtubule-binding protein that associates in situ with a subpopulation of stable microtubules. Interaction of this protein, now called GMAP-210, for Golgi microtubule-associated protein 210, with microtubules in vitro is direct, tight and nucleotide-independent. Biochemical analysis further suggests that GMAP-210 specifically binds to microtubule ends. The full-length cDNA encoding GMAP-210 predicts a protein of 1, 979 amino acids with a very long central coiled-coil domain. Deletion analyses in vitro show that the COOH terminus of GMAP-210 binds to microtubules whereas the NH2 terminus binds to Golgi membranes. Overexpression of GMAP-210-encoding cDNA induced a dramatic enlargement of the Golgi apparatus and perturbations in the microtubule network. These effects did not occur when a mutant lacking the COOH-terminal domain was expressed. When transfected in fusion with the green fluorescent protein, the NH2-terminal domain associated with the cis-Golgi network whereas the COOH-terminal microtubule-binding domain localized at the centrosome. Altogether these data support the view that GMAP-210 serves to link the cis-Golgi network to the minus ends of centrosome-nucleated microtubules. In addition, this interaction appears essential for ensuring the proper morphology and size of the Golgi apparatus. .
Figures



References (V体育平台登录)
-
- Abe A, Emi NN, Tanimoto M, Terasaki H, Marunouchi T, Saito H. Fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor β to a novel gene CEV14 in acute myelogenous leukemia after clonal evolution. Blood. 1997;90:4271–4277. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad FJ, Baas PW. Microtubules released from the neuronal centrosome are transported into the axon. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:2761–2769. - PubMed
-
- Alcalde J, Egea G, Sandoval IV. gp74, a membrane glycoprotein of the cis-Golgi network that cycles through the endoplasmic reticulum and intermediate compartment. J Cell Biol. 1994;124:649–665. - "V体育2025版" PMC - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网)
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"V体育ios版" Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

